TLDR
- Maple Finance is expanding the scope of DeFi by facilitating undercollateralized and uncollateralized lending.
- Maple provides an infrastructure that matches credit professionals, borrowers, and lenders. Their initial focus is on lending to market-neutral crypto trading funds, which are typically underserved by traditional finance.
- If Maple manages to build a robust and secure infrastructure, the benefits of using its platform will include the efficiencies of DeFi and smart contracts, immutable on-chain credit records, and transparent financial activity.
- While Maple has the potential to take DeFi to a far larger TAM, its product is riskier than overcollateralized protocols such as Aave and Compound.
- Undercollateralized and uncollateralized lending introduce default risk.
- Loans secured with off-chain assets and legal agreements may still take a long time to liquidate and reimburse lenders.
- Lenders must rely on the due diligence of Pool Delegates regarding the safety of the lending pool.
- Withdrawing liquidity from Maple pools is dependent on the amount of liquidity available in the pools, meaning lenders may not be able to access liquidity when they require it.
- Maple is currently lending to crypto-native trading funds, which arguably leaves them overexposed to the highly volatile crypto industry.
- That said, undercollateralized/unsecured lending is an important sector in DeFi, and the additional risk incurred corresponds with higher APY on their loans (compared to overcollateralized lenders like Aave and Compound).
Introduction
Innovation in DeFi lending has largely stagnated since the DeFi summer of 2020, with overcollateralized lending dominating. This has made sense in a high-risk and experimental environment. However, using an overcollateralized model is very inefficient in comparison to lending options available in traditional finance.
Maple Finance is expanding the scope of crypto lending beyond the overcollateralized model, with loans to real-world companies that are:
- Collateralized by real-world assets
- Undercollateralized
- Completely uncollateralized
Maple
Maple is building infrastructure to facilitate uncollateralized and undercollateralized lending of DeFi liquidity to businesses. Maple’s infrastructure provides a platform for interaction between credit experts, borrowers, and the wider crypto community as ‘lenders’.
Maple is targeting market-neutral trading shops that have limited access to traditional finance. Credit assessment and pool management are done by whitelisted industry professionals.
Maple currently has almost $1b in deposits, the majority of which is on Ethereum. However, Maple launched on Solana in April 2022 and has grown deposits to ~$115m in TVL already, with the stated intent of growing this to $1b by the end of the year. This appears to be a bet on the Solana ecosystem thriving alongside Ethereum going forward, and Maple’s decision to deploy there appears to be to gain first-mover advantage as a credit protocol in the Solana ecosystem.
Maple became profitable in Q1 2022, less than a year after launch. Read their full quarterly report here.
Key Participants
| Key Participants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borrowers | Primarily targeting market-neutral trading shops that have limited access to traditional finance. Borrowers are assessed and approved by Pool Delegates as having the capacity to pay back the loan. | |||
| Lenders | Users that can permissionlessly lend USDC to a pool of their choosing on Maple. | |||
| Pool Delegates | Pool Delegates are whitelisted professionals from the credit industry. Maple provides an infrastructure for Pool Delegates to attract and onboard global capital and get paid for doing so. |
How it works
 Source: Maple Finance Docs
Source: Maple Finance Docs
Pool Delegates
- Pool Delegates are whitelisted professionals from the credit industry. Pool Delegates assess the creditworthiness of borrowers, underwrite loans, and manage their lending pool.
- Examples of Pool Delegates include Maven11 and Orthogonal Trading.
- Maven11 recently published an update on the status of their pools on Maple Finance. Read the report here.
Roles
- Manage lending pools by performing due diligence and arranging the terms of the loan with Borrowers and servicing the loan book.
- Pool delegates develop a transparency investment strategy and underwriting process for assessing Borrowers.
- This strategy must be communicated to Lenders and is dependent on region, target Borrower industry, credit quality etc.
- Pool Delegate’s management of their lending pool also includes maintaining a sufficient stablecoin balance to enable withdrawals by Lenders.
- To align incentives, Pool Delegates are required to post at least $100,000 equivalent of MPL:USDC liquidity pool tokens to their lending reserve as a first-loss buffer.
- Note that this does not guarantee against malicious behaviour, as there is a possibility of receiving a more attractive offer by a colluding borrower.
- Pool Delegates also sign a contractual agreement to apply proper care and diligence in underwriting loans and management of the pool.
- Pool Delegates are required to manage liquidations. This involves the liquidation of collateral and Pool Cover via smart contract - depending on the collateral type and optimal course of action for lenders.
Compensation
Pool delegates are compensated by:
- Establishment fees
- Fee paid for the due diligence required prior to onboarding as a percentage of the loan value. The Establishment Fee is currently 1% annualized
- meaning it will be 1% for a 1-year loan, and 0.5% for a 6-month loan etc.
- This is split between the Pool Delegate (0.33%) and Maple Treasury (0.66%).
- Fee paid for the due diligence required prior to onboarding as a percentage of the loan value. The Establishment Fee is currently 1% annualized
- Ongoing Fees
- Fees for the management of the pool. Ongoing Fees are typically 10% of the yield received on the loan - but vary on a pool-by-pool basis. The Pool Delegate and MPL stakers receive Ongoing Fees.
Pool Cover
- Establishment fees
Maple enables anyone to provide pool cover to create more economic security for lenders. This pool cover serves as first-loss capital and is, therefore, the riskiest. As a result, rewards are higher.
This works as follows:
- Deposit liquidity to the Balancer 50:50 pool MPL:USDC. The depositor will receive Balancer Pool Tokens (BPTs) which are liquidity pool tokens that represent the deposit.
- Select a pool to provide the BPTs to.
Pool delegates are required to allocate at least $100k to their pool to align incentives. In practice, the Delegates have allocated more than $700k each and the roadmap for V2 includes the retention of Delegate fees to top up Cover.
- Note that this may be a trivial sum to pool delegates and does not fully remove the incentive for foul play.
This pool cover has been an issue with Maple so far. Although forcing participants to provide liquidity to the MPL token is potentially positive for the token value accrual - it impedes the user experience for Pool Delegates and cover providers generally. In addition to being first-loss capital, the pool can severely suffer from impermanent loss. The higher rewards are sometimes insufficient to even cover the impermanent loss. Furthermore, impermanent loss reduces the pool cover available in the event of default, making the loans riskier to Lenders. Therefore, for Maple to have a better product (as there will be increasing competition going forward) this measure will likely need to be reconsidered. In addition to this, should there be a default, MPL will need to be sold to cover the shortfall. This could increase the downward volatility of MPL as a default would already likely have a negative impact on price. Finally, the poor user experience for Pool Cover disincentivizes the provision of first-loss capital and therefore makes lending more risky. In the future, Maple intends on introducing more liquid assets that can be staked as pool cover e.g. USDC, WETH, and WBTC.
Note that Maple will be introducing xMPL as collateral for Pool Cover. This removes the risk of impermanent loss and gives additional utility to the token, however, the issue of sell pressure in the event of a default persists.
Borrowers
- Borrowers are businesses with well-established reputations and are assessed by Pool Delegates as having the capacity to pay back any loan.
- Borrowers enter into a Loan Agreement which enables legal recourse should the borrower fail to repay their loan.
- Current borrowers are trading firms and market makers.
- If a borrower fails to repay on time, there is a 5-day grace period before collateral is liquidated by the Pool Delegate. The Pool Delegate may exercise discretion to extend this slightly longer.
- It is important to remember that Maple is facilitating borrowing and lending between professional actors. The various nuances of lending can be managed by the Pool Delegate.
Lenders
- This comprises general crypto participants. Anyone can permissionlessly act as a lender to Maple pools (although permissioned pools will be introduced in the future). Lenders can simply deposit USDC to earn passive yield. Beyond this, lenders can also act as pool cover - whereby they deposit MPL:USDC liquidity pool tokens as first loss cover. This is analysed above in the Pool Cover section.
- Interest is earned from (1) the terms of the loan and (2) from MPL incentives.
- Lenders must select which pool(s) they would like to provide liquidity to.
- This is an important decision, as the likelihood that they will receive their full principal (and interest) back depends on the Pool Delegate’s due diligence and integrity in issuing loans.
- Note that lenders can withdraw interest at any time - depending on the availability of liquidity, and cannot withdraw their principle for for at least 100 days (90-day lock and 10-day cool-down period).
- It is possible that capital may still not be available after this cool-down if there is insufficient liquidity available.
- This is another consideration for lenders who may not be able to access their liquidity when required.
- This is now being seen in practice, and Maple highlighted on 20th June 2022 that there may be insufficient liquidity for withdrawals. Withdrawals are possible when (or if) the liquidity becomes available to the protocol.
MPL Token
Distribution
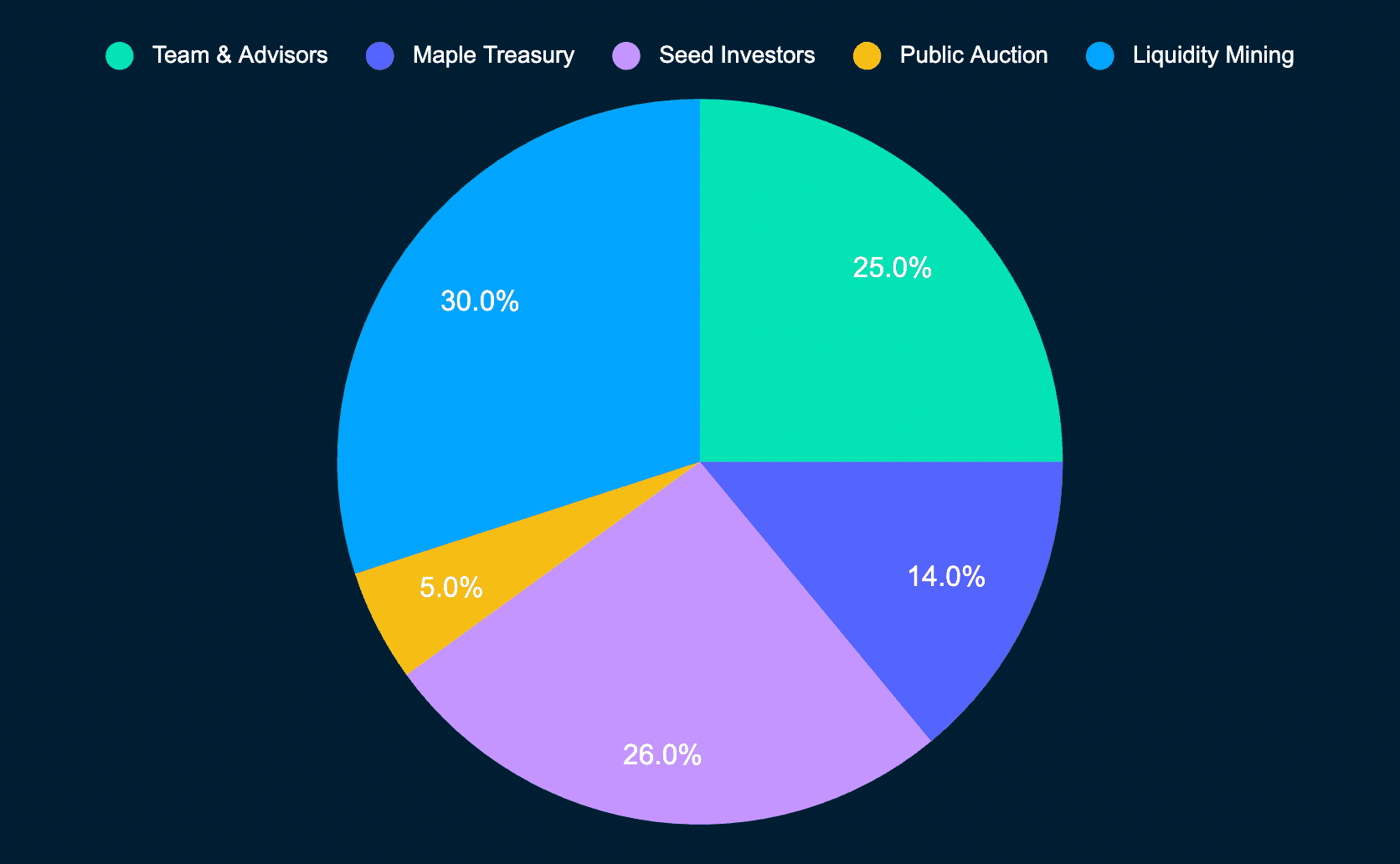
As can be seen, 31% of tokens were sold in the token sale - of which 26% were for seed investors. This figure is arguably higher than optimal.
In addition, the seed investors vesting schedule is an 18-month linear unlock and private investors have a 12-month linear unlocks. These unlock schedules are very short, and longer vesting schedules are more desirable as they better align the team’s incentives with that of the longer-term success of the protocol. On the flip side, the majority of tokens are now in circulation (~62%) meaning that the fast unlocking schedule means that MPL will not be as heavily diluted over the coming months and years compared to other protocols.
Furthermore, 25% of tokens are allocated to the team. The team has a 2-year vesting schedule, the majority of which will have vested after 18 months. This is arguably too short, as incentives wane after 2 years which is insufficient time to build a sustainable business (startup equity typically follows a 4-year unlock schedule). That said, the team appears to be fully committed to building Maple to become a major player at the intersection between DeFi and traditional finance. Notwithstanding this, the short unlock schedule should be borne in mind by anyone seeking to participate in the protocol.
This leaves 44% of tokens for the purposes of growth (30% liquidity mining, 14% treasury). Ideally, this figure would be slightly higher. However, Maple is a revenue-generating business and if successful, can have a self-sustaining treasury.
As of 23 June 2022, ~62% of MPL tokens are in circulation, with a $95m market cap and a $152m fully-diluted valuation. Most tokens are already in circulation, meaning that inflation will not heavily dilute the price. That said, in order to maintain the same price levels, the market cap will need to increase ~61% in value when all tokens are in circulation. If Maple succeeds, it is likely that MPL will far surpass this benchmark.
Utility
- Governance: despite centralized team control (which can make sense for a early-stage project), MPL token holders will eventually govern the platform. Governance is an ever-evolving field, and the final form this governance will take remains to be seen.
- Interest Rebate: Borrowers that stake sufficient MPL will qualify for a reduction in interest rate. This is sustainable as long as the protocol continues its market buybacks and redistributions to MPL stakers.
- Staking - xMPL: xMPL is based on the xSUSHI token model whereby protocol revenue is used to buyback MPL and redistribute it to MPL stakers. xMPL represents a share of the staking pool which accrues MPL rewards. This creates buy pressure on the token as revenue is generated. It is proposed that 50% of treasury revenues are used to buyback MPL for these purposes.
- xMPL Pool Cover: xMPL token will be used as Pool Cover for the lending pools.
If their tokenomics are implemented as outlined, MPL can have far better token utility than the majority of DeFi tokens. The team is pragmatic - and introduced a number of improvements already this year. They will likely seek to refine this over time. The token may be at risk of being classified as a security in the future by overzealous regulators, and some protocols have opted against an xSUSHI token model for this reason. However, this is dependent on how future regulation of the space develops. The Maple team will certainly be increasingly visible to the financial world if it progresses beyond crypto firms.
A High-Level Walkthrough of Maple
- Pool Delegate onboards.
- Borrower creates borrower profile and interfaces with the Pool Delegate who conducts private diligence on terms directly with the borrower.
- If terms are agreed upon, the borrower can launch a loan contract. The Delegate creates a lending pool and activates it by posting pool cover as MPL:USDC and/or xMPL.
- Lenders can provide liquidity to a pool of their choice, and/or provide pool cover as well (in BPTs or xMPL).
- Borrower draws down the loan and pays an establishment fee which is accrued to the Maple Treasury and Delegate.
- Borrower pays interest in accordance with a repayment schedule and pays principal at maturity.
- Delegate claims interest on behalf of the pool throughout the loan term and claims principal with final repayment upon maturity.
Potential Growth
As an infrastructure provider, Maple is looking to onboard an increasing number of institutions - both on the borrower and Pool Delegate side. Due to professionalized credit assessment, KYC requirements, and legal recourse available - Maple could present an attractive (albeit risky) alternative for DeFi users to generate yield. The Maple team uses the Shopify analogy to describe their business. Shopify merely provides a frontend for businesses to take their business online. Likewise, Maple provides an infrastructure for institutions and credit experts to work together and access DeFi liquidity. If Maple can avoid serious negative events, diversify its borrower profile, and stay on the right side of regulation, an increasing number of borrowers, pool delegates and lenders could flock to the platform - creating a strong network effect and moat. However, this is far from guaranteed. Onboarding more non-crypto borrowers will be critical which can have a snowball effect. However, it is probable that greater legal certainty will be required for this to happen at scale.
A number of DAOs have diversified their treasuries into Maple’s pools which can be a short-term driver of growth. Progress on non-crypto businesses will be important for Maple to provide lenders with yields that are uncorrelated with crypto markets.
Risks
Maple’s primary risks are smart contract risk and default risk.
Smart Contract Risk
Smart contract risk is self-explanatory, and Maple has undergone 4 audits - from Trail of Bits, Peckshield and Dedaub. A number of vulnerabilities were found, all of which the team have claimed to address.
These audits can be viewed here.
Default Risk
Default risk is well worth considering as most DeFi protocols do not deal with this - there is virtually no default risk on Aave and Compound. Therefore, it is not desirable to put a significant proportion of one’s portfolio into Maple and the additional default risk must be adequately compensated for with enhanced yield.
Furthermore, an investment in a Maple pool is a bet on the Pool Delegate’s ability to properly assess the borrower’s risk profile. Risks here include suboptimal due diligence, fraudulent activity from the borrower, and fraudulent collusion between the Pool Delegate and the Borrower. Care must be taken when selecting which pool to lend to. While legal recourse is available, these risks remain tangible. Finally, Q2 2022 has shown clear weaknesses in the crypto market - with 3AC, Defiance, and Celsius on the verge of insolvency. As Maple is currently exclusively lending to crypto businesses that have been assessed as being creditworthy, it is noteworthy that crypto market conditions have changed drastically to the downside and the financial health of these companies may have decreased. Note that given the focus is on market-neutral trading companies, high volatility can equate to high returns. However, in a prolonged bear market with limited volatility, such firms may struggle.
Maple is arguably overexposed to crypto companies, and despite being a logical starting point for bootstrapping the protocol it would be desirable for them to diversify to other industries. This problem has become evident recently, with Babel Finance (a recipient of a $10m unsecured loan) suspending withdrawals and redemptions citing liquidity issues. While it remains to be seen whether or not they will be able to repay this loan, it highlights the problem of overexposure to such a volatile industry.
Regulatory Risk
Maple is at the cutting edge of DeFi innovation by venturing into undercollateralized and uncollateralized lending. It is providing retail investors with access to yield from lending products that are managed by professionals. There are currently no barriers to investing in Maple pools. Others have taken a more cautious approach, by requiring KYC and barring US-based individuals/entities. Given the objective risks of lending on Maple, the protocol could come under increasing regulatory scrutiny especially if/when it scales out to non-crypto industries.
Team
Maple has a strong team, many of which have previously worked in traditional finance. This is desirable, as Maple is building the infrastructure for integrating traditional finance and DeFi liquidity and requires people that understand the space. The team has grown significantly over the past year and is fully doxxed.
Check out the team on LinkedIn here.
Takeaway
- Maple is building infrastructure for onboarding debt capital markets to DeFi. This is an underdeveloped market with enormous potential.
- Maple’s infrastructure simplifies access to DeFi liquidity and includes prerequisites such as KYC, legal recourse, and professional credit analysis that are required for undercollateralized/unsecured lending. It is building key infrastructure to professionalize DeFi and take it to the next level.
- Maple’s customers at present are crypto-native trading firms that struggle to access traditional financing. This is a starting point that makes sense, however, Maple will need to move out of this relatively risky segment to fulfil its potential. Overreliance on crypto firms will likely have negative outcomes over a prolonged bear market, which could severely reduce confidence in Maple. It will be interesting to observe if Maple’s current debtors manage to repay the full loan amount in such harsh market conditions.
- This is a critical period for Maple that could have far-reaching consequences for lender’s confidence in the platform (positive or negative).
- Maple has published their intent to improve MPL’s utility which should give it far greater fundamental value than the majority of other tokens, making it crucial to the proper functioning of the protocol. However, selling pressure in the event of default (due to pool cover design) and potential regulatory issues will need to be overcome.